Cloud technologies are rapidly becoming one of the significant investment avenues for organizations, regardless of their size and industry. Today, companies are looking for a mix of enterprise & cloud-based apps that best facilitate business-oriented outcomes. And, for that, they have embraced cloud-based integration at some stage. The reason is that without proper tools to manage data in the cloud, this information can become siloed, overlooked, or lost altogether. This is because more & more business operations are happening in the cloud – either hybrid or fully cloud-to-cloud environment.
With specialized platforms and as-a-service capabilities, companies can design and deliver solutions faster while resolving complex operational challenges.
This article will explore the key features (and benefits) of cloud application integration, available platforms, use cases & more to enable you to create your integration strategy.
What is Cloud Integration?
It is the process of bringing data from different sources into a unified platform. It breaks down software silos to allow easy access & management of business apps and data from disparate systems in real-time.
In the modern business ecosystem, the more applications a business uses daily, its IT environment becomes more complicated. Therefore, it is often worth deploying cloud integration platforms before application volumes increase exponentially. Cloud integration platforms accelerate connectivity, enhance visibility & ultimately optimize key business processes – in one place! The demand for cloud system integration emerged from this need to combine and maintain disparate data sets and cloud resources while unifying different cloud environments with on-premises data.
And, while integration can be managed in-house by deploying infrastructure and services that support cloud connections – this approach could prove to be time-consuming and costly, even for larger enterprises. Cloud integration platforms help streamline this connective process & further reduce the amount of lead time required for deployment. Cloud integration puts businesses in a much better position to manage and optimize their processes, operations, and customers. Depending on the needed volume and data transfer speed, IT teams can leverage the following types and methods of cloud integration.
How Does Cloud Integration Work?
Let’s explore a structured framework of the cloud integration process that guides you through the key stages from planning to implementation.
- Uncover the Integration Need: Defining the primary objective behind the integration of the cloud further makes things more transparent and easier to operate. In this step, you can include specific reasons, challenges, and issues to resolve and list out systems like CRM, ERP, and others. , and then map data flows (source, destination, format).
- Choose the Ideal Approach of Integration: Secondly, while making a decision of cloud integration to leverage its modern capabilities consider your business needs and resources. Among the PI Integration, iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) and custom Integration make the best choices by assessing factors like integration complexity, budget, technical expertise, and scalability.
- Design and Develop Integration Flow: The next step starts with mapping data flow and how data will be processed, transformed, and mapped between various systems, solutions, and platforms. Set integration logic with a sequence of events and trigger for effective and timely data transfer.
- Test and Deploy: Once done with the integration process, you can move further with pilot testing using a small group of users to identify issues before actual and full deployment takes place. Next, follow User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and after successful verification and validation, proceed with deployment into the production environment.
- Monitor and Maintain: Finally, monitor performance for ongoing improvement and efficiency. Conduct regular audits and performance analyses, focusing on key metrics to efficiently address emergency issues or operation-halting reasons and ensure seamless connectivity.
Types of Cloud Integration
Cloud-based integration would include cloud-to-cloud integration, cloud-to-on-premises integration, or a combination of both. Further, cloud integration solutions address different business components, including data and applications. And IT teams can leverage the listed below types of cloud integrations, depending on the data transfer volume and speed;
- Cloud Data Integration: Enables seamless data flow between different repositories. It involves processing, transferring, and transforming information in batches, or in real time during integration. Businesses typically leverage data integration to transfer raw, unstructured cloud data for specific use cases. However, IT teams can also centralize cloud data with mainframe system data or legacy servers. Examples include business analytics, master data management, artificial intelligence training, and ELT (extracting, loading, and transforming) raw data into a data lake or warehouse. Data integration tools are designed to perform activities such as data cleansing, data quality checking, masking, and batch processing.
- Cloud Application Integration: Unites numerous applications and ensures continued interoperability and functionality. It involves applications sharing requests, commands, and other mechanisms to trigger business activities. This process facilitates data exchange using real-time dataset integrations between the systems involved. Common examples include integrating critical business apps such as inventory management, sales reporting, customer relationship management, and financial applications. It helps businesses optimize their workflows, build insight-driven data models, predict future demand with machine learning models and modernize their infrastructure.
Benefits of Cloud Integration
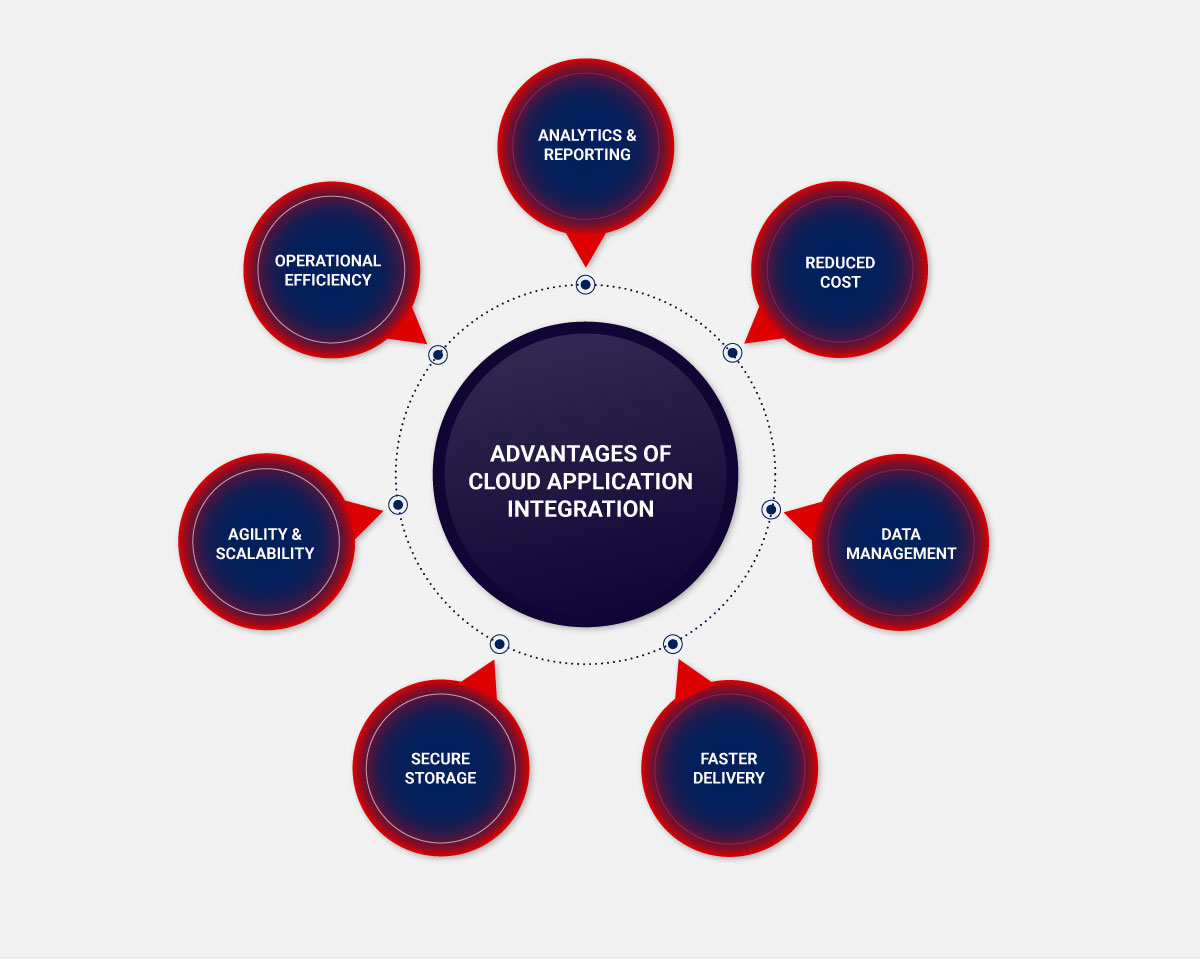
Cloud integration with different enterprise applications offers multiple advantages over time-consuming traditional information and data exchange infrastructure methods. It removes data access barriers by facilitating deeper analytics and increased collaboration. And cloud integration software helps you counter data silos by synchronizing the data and applications. Organizations adopt cloud system integration to improve functional connectivity and gain comprehensive data access. The market for cloud integration platforms is expanding rapidly, and so it’s no surprise that industry leaders are leveraging their benefits in the following ways:
- Analytics & Reporting: Companies can avoid redundancy even with a shared data store to reduce storage costs and synchronization efforts. You would agree that the advent of business intelligence enables organizations to utilize data gathered from mining and discovery to improve overall performance. Did you know cloud integration provides a path for robust data analytics platforms, CRM systems, and other applications hosted by third-party providers? It enables the linkage of data stored on local servers with remote sources.
- Reduced Cost: A cloud integration platform is easy to implement, manage and deploy integrations. It is far more affordable than outsourcing an IT specialist to set up a solution from scratch or hiring dedicated resources to manage it in-house. Conventional integration solutions necessitate the creation of custom connections to third-party apps, which can be costly and complicated.
- Data Management: By leveraging iPaaS (Integration Platform as s Service), a business can host its integration technology in the cloud instead of a firewall. It facilitates swift B2B data exchange and management in real time. Accessing the correct data at the right time is vital to better decision-making.
- Faster Delivery: B2B ecosystems are expanding exponentially, making it imperative to connect with new customers and partners immediately. Modern businesses are moving faster by shifting their key workflows and integration flows to the cloud. The integration enables applications to exchange real-time data, make crucial decisions quickly, and deliver services instantly.
- Secure Data Storage: On-premises setups store all the information on physical machines. So, if the machine breaks down, all the data may be lost. Cloud platforms prevent such issues with secure data storage that can be easily accessed on any device at any time.
- Agility and Scalability: Businesses are better equipped to evolve and adapt to market and consumer demands when using the cloud. The extensibility, interoperability, and cost-efficiency offered by cloud integration platforms make scaling IT infrastructures much easier, faster, and more flexible than upgrading on-premises physical hardware. With cloud platforms, everything is digitalized in a fraction of the time – from reducing compute power to expanding server space. Businesses can remain agile when provisioning IT resources for enterprises and leverage deploying flexibility for modern apps while connecting business services.
- Operational Efficiency: Since business processes are integrated with cloud platforms, users can shift their focus from searching for information to analyzing it in real time. The cloud is unlikely to experience downtime so that IT teams can be more productive, and businesses can save on maintenance. Lastly, users can easily automate manual data entry, reporting, and information restructuring processes with intelligent operational workflows to avoid human errors.
With the cloud, organizations benefit from a holistic view of all the essential and most complex business scenarios within their business environment. The insights help create and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Cloud Integration Challenges
Organizations need to choose the right integration platform to enjoy the advantages of cloud integration. However, that does not eliminate an organization’s possible challenges with integration priorities. At Rishabh, we’ve assisted several enterprises with their vital decision to move to the cloud. Below are some crucial challenges we can help you to address during your journey.
- Data Security: The enterprise data gets stored and processed by a third-party vendor making it vulnerable to theft, leakage, and unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Depending on the industry type, particular laws might regulate how consumer data is shared and stored.
- Lack of Standardization: Cloud platforms, applications, and resources use different data schemas and formats to communicate with various elements.
- Data Movement: It can be an error-prone and time-consuming process depending on the volume, variety, and frequency of data transfer.
- ETL Workflows: Cleaning, treating, processing, and transforming raw, unstructured, and structured data adds complexity and decelerates the integration process.
- Network Latency: Cloud environments with high latency often limit integration workloads.
Deploying the right tools and having an experienced technology partner, like Rishabh Software, is vital to implement a seamless cloud integration process. More and more businesses starting with cloud integration are opting for iPaaS solutions. It helps them integrate cloud-based applications & systems with domain-specific capabilities around ecosystem enablement, IoT, and mobility.
While these challenges may seem daunting, organizations can overcome them by implementing proven best practices that address each obstacle systematically and proactively.
Cloud Integration Best Practices
Cloud-based integration demands a systematic and well-defined approach with the right set of practices for success. From research to collaboration, decision-making, and re-evaluation, every step reflects your approach to cloud integration. Here are some crucial best practices to consider.
- Focus on Planning: A properly designed integration plan leads to effortlessly executed procedures that drive ongoing achievement. The team must establish objectives and then analyze system compatibility to develop an executable execution framework. For example, an e-commerce company integrating CRM and ERP systems should outline data flow, dependencies, and security measures before execution.
- From the Beginning, Make Data Security a Priority: Data security should be a core focus throughout the integration approach and cycle. Thus, in order to keep sensitive data protected, the smart implementation of modern methods like encryption, user-based authentication, and compliance standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Choose the Set of Right Tools: The selection of proper integration tools, including iPaaS, API gateways, and ETL tools, decreases operational complexity while simultaneously reducing project development demands. SaaS organizations deploy MuleSoft and Dell Boomi approaches to enable cloud-to-cloud integration without the need for time-consuming custom programming.
- Adopt a Modular Approach: Design integrations as independent modules to improve flexibility and scalability. This allows for incremental upgrades without disrupting the entire system. A logistics firm integrating its order management and tracking systems can build separate modules for inventory sync, shipment updates, and customer notifications.
- Prioritize Real-Time Data Sync: Strategic decision-making processes alongside operational performance get improved through real-time data synchronization. For example, a fintech company that merges payment gateways with accounting software delivers immediate transaction updates, which reduces reconciliation times.
- Implement AI-Driven Automation: Uses predictive monitoring in combination with anomaly detection to enable automated troubleshooting through AI. For example, AI-powered BTC tech monitors power consumption patterns to alert users when distinct usage patterns arise, prompting automatic system adjustments.
- Emphasize API Governance: Establish standards for API management, versioning, and security to maintain consistency. For instance, a retail business integrating multiple third-party vendors can enforce API rate limits and authentication protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
- Leverage Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Strategies: Integrating multiple cloud environments enhances flexibility and prevents vendor lock-in. A media streaming company, for instance, might use AWS for content storage and Google Cloud for AI-driven recommendations, ensuring optimal performance.
Elements of Cloud Integration
Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
The Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) stands as a foundational cloud element that gives businesses complete access to the cloud ecosystem to efficiently build, deploy, and operate integration workflows. The integration platform as a service lets applications connect from premises deployments to cloud software while minimizing hardware and middleware requirements to deliver easy integration across platforms.
The deployment process gets accelerated through iPaaS so businesses can introduce their new apps and services into markets faster than ever. The integration platform as a service uses standardized frameworks to reduce both overall integration expenses and foster scalability, which enables businesses to meet evolving technological needs and enhance data capacities at reduced supplementary financial requirements. Through its designed structure, iPaaS enables enterprises to boost operational effectiveness while optimizing complicated workflows to fulfill their strategic technical requirements.
API Management
API management is a crucial part of cloud integration, overseeing the end-to-end lifecycle of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) while ensuring a secure and scalable environment. APIs enable different software, solutions, and applications to communicate and share information as well as functionality. The process involves multiple stages, including creating, publishing, and monitoring APIs to ensure they remain reliable, consistent, and secure for effective management.
This not only simplifies operations by integrating multiple cloud and on-premise services but also enhances information availability for users and stakeholders across the business. Additionally, insights gained from API management tools can help businesses optimize API usage and performance, making the overall technology ecosystem more agile and efficient.
Middleware
Middleware plays an essential role in cloud integration. It serves as a middle layer that enables different apps, services, and databases to talk to each other and work together without a hitch. It acts as the “glue” that holds various systems together, making data sharing and teamwork possible. This helps companies link their old apps with new cloud options. This integration is key to maintaining data flow and ensuring business tasks run well across different setups. Middleware provides important services like message queuing, handling transactions, and changing data formats.
These services boost how apps work and make them easier to use. In mixed setups where both in-house and cloud apps exist, middleware tackles connection issues. It helps smooth teamwork and data sharing. By using middleware well, companies can get the most out of their tech tools and adjust to changing work needs. This makes them more flexible and quicker to respond overall.
Cloud Integration Platforms & Their Key Capabilities
The said platforms help integrate cloud-based applications & systems with domain-specific capabilities around ecosystem enablement, IoT, and mobility.
Let’s have a look at top integration platforms,
- Zapier: Provides code-free application integration to expanding companies. With the ability to connect to and share data with 1,000+ web apps, it can automate almost any business workflow.
- MuleSoft Anypoint: Empowers management of all the application programming interfaces (APIs) and integrations over a centralized platform. It provides various tools for developing, managing, and testing APIs. Leveraging edge gateways and encryption ensures data protection and administers access rights.
- Dell Boomi: Allows fusing the apps, data, and processes into one. It helps manage data quality governance, application integration, and B2B network and build workflows with minimal coding.
- IBM App Connect: An all-in-one integration tool that enables the admin to create workflows that decide how data is transferred from one application to another.
- Microsoft Azure Logic Apps: Enables administrators to automate workflows that integrate apps and business data across on-premises systems and cloud services.
- Workato: Enables enterprises to automate business workflows, integrate their apps, and extract real-time insights. Its compelling visual interface logic automation presentation is easy to follow.
Businesses can also leverage the embedded technologies of these platforms to natively communicate beyond business boundaries and enable seamless integration & movement of data between services and customer systems. These B2B tools and features create a secure data gateway into a SaaS architecture to allow smooth, faster & reliable information exchanges. The right cloud platform enables IT teams to make changes on the fly and allows complete configuration across the entire ecosystem.
Choosing a cloud integration platform for your business needs becomes easier when you know the essential elements. Listed below are the key components & capabilities of a comprehensive cloud integration platform to help you make an informed choice:
- Built-in Connector: Leverages API integration features for efficient management of complex environments
- Automation: Seamless integration of online services improves productivity and client experience
- Virtual Infrastructure: Streamlines integration operations without needing custom coding.
- Speed: Enables quick and easy connectivity for integrating apps, data, and systems
- Security: Safeguards confidential and sensitive data from unauthorized users
Cloud Integration Use Cases
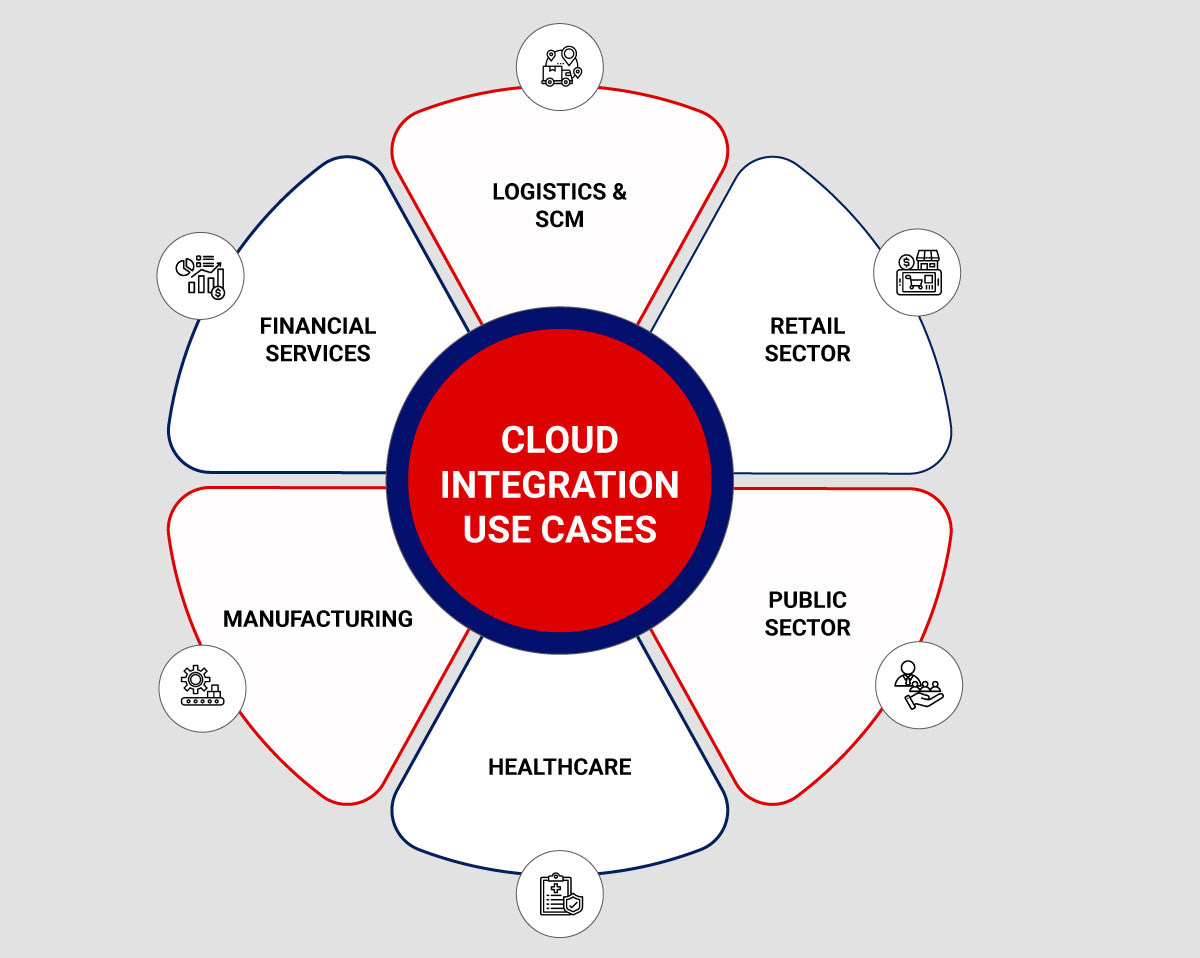
Cloud integration is perfect for sharing analytics tools and data between users from different locations. It can reduce data redundancy, automate workflows, and orchestrate APIs and services. Companies can also use IoT connectivity and AI models to connect their assets and offerings with partners and customers quickly. While the application of cloud integration remains the same across business verticals, the prominent use cases vary.
- Financial Services: The sector helps centralize their savings, checking, mortgage, credit and debit card, and CRM data. It would enable employees to better understand the client’s financial needs, improve the service experience & optimize the offerings to cross-sell or upsell.
- Logistics & SCM: Freight management, equipment utilization & tracking the frequency of transits are all essential tasks. Transportation businesses must collate and synchronize data from different sources to optimize resource use or scale down as and when needed. Cloud integration enables an accurate analysis of key performance metrics, delivering dependable results with minimum scope for glitches.
- Retail Sector: Brick-and-mortar stores are now pivoting to online channels with new apps for order management, shipping, inventory tracking & payment processing. These apps must ingest, integrate, and exchange data for seamless online shopping. Cloud based integration enables retailers to digitize their business, connect these apps and transfer data in real-time.
- Public Sector: State and federal governments can leverage cloud integration solutions to offer online services. Departments of motor vehicles and police departments can benefit from cloud application integration while allowing online vehicle registration renewals, permit home remodels, federal taxing, and voter registrations.
- Healthcare: Data silos can adversely affect the quality of patient care. Cloud integration allows interoperability, strengthens provider communication, and enables patient-first maintenance. It also allows patients to easily access their health records with apps that aim to improve treatment adherence and patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: It unifies data from engineering systems, assemblies, inventories, supply chains, and shipping. And this data integration would help companies efficiently manage production quantity and quality.
How Rishabh Can Help You Make the Most of Cloud Integration
Cloud-based integration encompasses; 1) cloud-to-cloud integration, 2) cloud-to-on-premises integration, and 3) a combination of both types of integrations of both applications and services. And for businesses, iPaaS enables the utilization of both integration solutions through a responsive, scalable, and reusable cloud integration platform.
As an experienced cloud-based application development company, our cloud integration services cover creating holistic strategies, migrating your applications and workloads to virtualized environments, or refactoring them for more efficient utilization. Whether you need fast integration with AWS or Azure or want to create cloud applications from scratch – we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does cloud integration differ from traditional integration?
A: Cloud-enabled applications are built with the capability to exchange data in real-time within or across the cloud ecosystem, empowering businesses to embrace greater flexibility and scalability. In contrast, traditional integration relies entirely on on-premise systems, requiring more effort for updating and maintaining data flow.
Q: What are the security considerations in cloud integration?
A: Critical security considerations include end-to-end encryption (in transit and at rest), robust IAM implementation with role-based access controls, and compliance with relevant regulatory frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.). Organizations must implement secure API gateways, maintain comprehensive data governance policies, and establish strict vendor security assessment protocols. Regular security audits and robust DR/BC procedures are essential for maintaining the integrity of integrated cloud systems.
Q: Which industries benefit most from cloud integration?
A: Almost every industry is leveraging cloud integration and exploring its benefits. However, major industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, fintech, and others are at the forefront of adoption.











 30 Min
30 Min


