Edge computing and cloud computing are two different approaches to computing and data management, each with its own unique benefits and drawbacks. The edge-based processing approach minimizes latency and reduces bandwidth use by handling immediate tasks locally, while cloud’s vast resources and remote accessibility provide flexibility and power for long-term data processing, storage, and analysis.
This distinction is crucial because it impacts how fast data is handled and how much control you have over it. So, getting a detailed understanding on both edge and cloud computing is important to optimize IT infrastructure and make the best use of both.
This article highlights the key comparisons between edge computing vs cloud computing, their similarities, pros & cons, and use-cases to help you make an informed decision.
What is Cloud Computing?
It represents a transformative approach to accessing and utilizing IT resources. It involves the convenient delivery of technology services over the Internet, eliminating the need for investing in physical infrastructure like data centers and servers.
What is Edge Computing?
It is a new way of handling information that refers to a range of networks and devices at or near the user. It’s all about processing data right where it’s made, which helps process things faster and handle more information. This quick processing means you can take faster actions and get immediate results.
Difference Between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
Both these approaches serve crucial roles in the digital ecosystem. Their differences in processing location, latency, scalability, use cases, security, and reliability cater to distinct needs and applications of different industries and organizations. So, let’s explore the detailed difference between cloud computing vs edge computing:
Location of Processing
- Cloud Computing: Under this technology, centralized data processing takes place in remote data centers managed by cloud service providers. These data centers could be situated in different geographical locations, serving users globally.
- Edge Computing: This distributed computing framework processes data closer to the point of generation, typically on local devices or servers at the edge of the network. This reduces the distance data needs to travel, enhancing speed and reducing latency.
Latency
- Cloud Computing: Due to the physical distance between users and remote data centers, there might be higher latency as data travels back and forth across networks.
- Edge Computing: As the data is processed closer to the data source, latency is significantly reduced. This enables faster response times, which is crucial for real-time applications.
Scalability
- Cloud Computing: It offers extensive scalability, allowing users to access vast amounts of resources on-demand. Cloud services can easily accommodate a high volume of users and data.
- Edge Computing: While it can be agile, the scalability of this computing platform may be limited by local resources available at the edge devices or servers. Scaling might require additional infrastructure deployment at multiple edge locations.
Use Cases
- Cloud Computing: It is Ideal for applications that require substantial computational power, extensive storage, and accessibility from anywhere with internet connectivity. Common uses include big data analytics, AI/ML processing, and hosting applications.
- Edge Computing: Fog/Edge Computing is suited for scenarios where low latency and real-time processing are critical. Applications include IoT sensors & smart devices and remote monitoring systems.
Data Security and Privacy
- Cloud Computing: It involves centralized data storage which can raise valid concerns regarding data security and privacy. Despite these concerns, cloud providers implement robust security measures aimed at safeguarding stored data.
- Edge Computing: The data that is processed at the edge can enhance security by minimizing the need to transmit sensitive data to distant servers. However, securing numerous edge devices presents its own set of challenges.
Reliability
- Cloud Computing: Generally, this computing framework offers high reliability due to redundancy and backup systems in place within data centers.
- Edge Computing: The reliability of distributed systems might vary depending on the quality and maintenance of edge devices or servers. Thus, making it crucial to ensure stability in these distributed systems.
Similarities Between Cloud and Edge Computing
Despite the differences in their approach, they share notable similarities. Both edge and cloud computing aim to enhance accessibility, scalability, and efficiency in handling information. Understanding their similarities provides insights into how these two approaches complement each other, contributing to a more robust and comprehensive computing landscape.
| Parameter | Shared Similarity |
| Data Processing | These platforms facilitate data processing, although at different levels (edge for real-time, cloud for large-scale) |
| Scalability | Both offer scalable solutions, though Edge focuses on device-level scaling and Cloud on virtual resources |
| Automation & Analytics | This platform leverages automation and analytics tools to extract valuable insights from data |
| Pricing Models | Cloud and edge computing both have flexible pricing models to cater to varied usage requirements |
| Security Focus | Both platforms prioritize data security, demanding robust measures tailored to their respective architectures |
| Collaborative Potential | Edge and cloud computing present unique capabilities that complement each other for optimal data handling |
Pros and Cons of Edge Computing
Choosing between cloud and edge computing depends on your specific needs and priorities. Consider factors like latency requirements, data sensitivity, budget constraints, and application complexity to make the best decision. Let’s dive deep into the detailed pros and cons of edge computing to help you make the right decision.
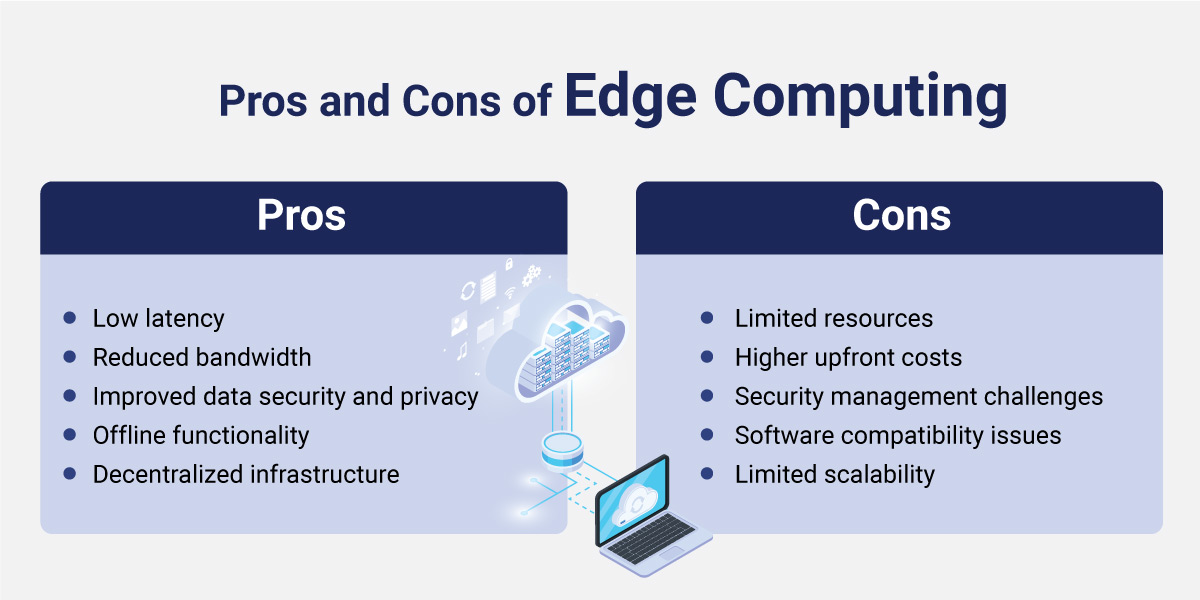
Pros
Low latency
The traditional approach impacts real-time performance due to delay in data processing, whereas edge computing is a game changer that drastically reduces the time it takes for information to travel to and from a central server, making it ideal for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Reduced bandwidth
Sending large amounts of data back and forth to the cloud consumes significant bandwidth, leading to potentially high internet bills. Edge computing technology significantly reduces bandwidth usage by processing and filtering data locally, while only sending essential information to the cloud. This results in substantial cost savings, especially for businesses generating or handling large data volumes.
Improved data security and privacy
By reducing the amount of data transmitted and processed in the cloud and keeping the sensitive data on-site, edge computing helps in minimizing the risk of breaches and leaks in centralized cloud servers.
Offline functionality
Every organization aims for uninterrupted functionality in remote or disconnected environments. This computing approach does the same thing for you. You can operate your connections and devices when interconnectivity is lost. It is helpful for scenarios like disaster relief or remote operations.
Decentralized infrastructure
Instead of a centralized system, edge-based processing distributes processing power and storage capabilities to smaller, localized nodes located closer to the data source. This makes the system more resilient to failure in one location as processing and storage are distributed.
Cons
Limited resources
Individual edge servers have less processing power and storage capacity compared to the vast computational power and storage capacity of centralized cloud servers. This restricts complex computation or large data storge on this computing platform.
Higher upfront costs
Setting up and maintaining edge infrastructure can be expensive as it requires a distributed network, specialized hardware, and network upgrades. So, it is advisable to perform a careful cost-benefit analysis specific to your application and needs before choosing any computing platform.
Security management challenges
Maintaining stringent security in edge computing devices becomes complex due to their numerous endpoints spread across diverse location. So, it is challenging for edge computing devices to implement robust security measures like encryption, intrusion detection, and endpoint protection software.
Software compatibility issues
Different edge devices may require specific software, such as processors, operating systems, and memory capabilities, making it difficult to develop and deploy software that runs seamlessly across all of them. This becomes a challenge in edge computing to manage large deployments.
Limited scalability
Expanding edge computing capacity can be more complex and expensive than scaling cloud resources. This constraints its scalability and limits its ability to handle massive data loads or complex computations.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
This centralized computing approach offers unparalleled advantages such as scalability, cost-efficiency, and centralized management and control. However, alongside these benefits, there exist certain drawbacks worth considering. Let us explore its pros and cons to help your organization make informed decisions for leveraging cloud computing’s transformative potential.
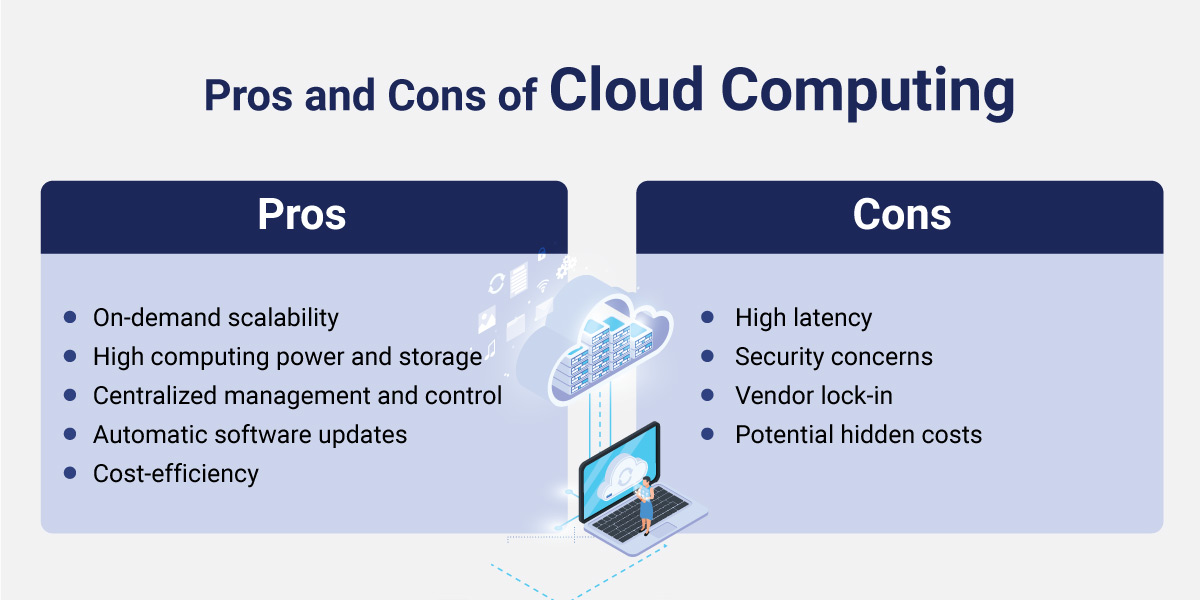
Pros
On-demand scalability
The flexibility it offers is one of its key strengths. You can easily scale up or down cloud resources to meet the fluctuating demand of your business. This agile and flexible approach to the cloud makes it cost-effective and efficient for your business.
High computing power and storage
It offers access to powerful servers and vast storage capacity. This ability helps in analyzing massive datasets with ease and easily run large-scale applications.
Centralized management and control
This computing approach help organizations with simplified IT management and enhances visibility with bird’s-eye view of their entire cloud environment. It simplifies the management of applications and data across the entire system from a centralized platform.
Automatic software updates
Cloud providers handle regular software updates and maintenance tasks. This minimizes downtime and reduces the workload of internal IT team, This frees up their time for other critical tasks such as business growth plans and working on key projects.
Cost-efficiency
The pay-as-you-go pricing model eliminates the requirement for large initial investments in hardware and infrastructure, allowing companies to pay solely for the resources utilized. This approach enables organizations to create better budgeting strategies.
Cons
High latency
Data and applications are hosted on remote servers and accessed over the internet. The data travels to and from the cloud, which leads to slower response times, making it unsuitable for real-time applications.
Security concerns
Cloud computing is based on a shared responsibility model so the potential for vulnerability, cyberattacks and data breaches is a point of concern.
Vendor lock-in
Vendor lock-in poses challenges when transitioning between cloud providers due to intricate and costly data migration processes, often complicating the shift.
Potential hidden costs
Unexpected expenses may arise, including cumulative fees for bandwidth usage, data storage, and specialized services, impacting budgeting plans and adding unforeseen financial burdens.
Use Cases of Edge and Cloud Computing
These two computing approaches are redefining industries and enabling groundbreaking applications across healthcare, retail, manufacturing, finance, and transportation sectors. Here’s a breakdown of specific use cases and how they leverage the full potential of data, optimize operations, and deliver exceptional experience to the end-users.
Retail
- Edge Computing: Using smart cameras placed at store entrances to quickly analyze customer details. This helps to instantly adjust displays or create targeted promotions in real-time, improving the shopping experience.
- Cloud Computing: In-store sensors collect detailed data on product movement and customer behavior. This data is sent to the cloud for analysis, facilitating optimal inventory management and store layout adjustments based on broader trends and patterns.
Manufacturing
- Edge Computing: Edge devices like IoT sensors, smart cameras, and IoT gateways installed on factory machines monitor their performance in real-time. They proactively detect potential breakdowns, allowing for timely predictive maintenance and preventing disruptions in production.
- Cloud Computing: Data collected from various machinery sources on the factory floor is gathered and processed in the cloud. Advanced analytics help identify long-term patterns and areas requiring improvement, enhancing production efficiency and economic productivity through optimized operations.
Healthcare
- Edge Computing: Within the healthcare industry, hospitals and clinics use wearable devices to continuously monitor patients’ essential signs, instantly alerting medical professionals to critical changes. This real-time data transmission is invaluable, particularly in remote areas, ensuring immediate attention when needed.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is essential in healthcare for accessing and analyzing imaging data and electronic health records (EHR). This technology speeds up diagnoses, customizes treatment plans, and encourages collaborative research. Overall, it improves patient care and drives advancements in the medical field.
Transportation Industry
- Edge Computing: Autonomous vehicles rely on this decentralized computing approach for instantaneous obstacle detection and collision avoidance. This real-time decision-making makes them safer and more responsive on the roads.
- Cloud Computing: Traffic cameras and sensors across the transportation network feed data to the cloud. This data fuels intelligent traffic management systems, optimizing traffic flow, reducing congestion, and enhancing overall commuting experiences for everyone.
Cloud vs Edge Computing – Which One to Choose and When?
The decision between Cloud and Edge Computing depends on the specific requirements of organizations. Consider the following factors:
Latency Sensitivity: Applications requiring real-time responses benefit from edge-based processing.
Data Sensitivity: For sensitive data, edge computing is preferred as it offers localized processing, enhancing security.
Scalability Needs: When on-demand scalability is a priority, cloud computing excels in scalability and flexibility for fluctuating demands.
Sometimes, using a mix of both cloud and edge technologies works best. This way, you can get the advantages of both and make things work well, like being fast, scalable, and cost-effective, based on your task or business needs.
Why Choose Rishabh Software for Cloud Application Development?
We are a strategic partner for organizations seeking expertise in cloud technology. With over two decades of experience, we specialize in developing holistic cloud strategies, incorporating architecture design and development that combines components and utilizes resources distributed across the network. This approach ensures that your cloud infrastructure is optimized for efficiency and effectiveness.
We offer a comprehensive suite of services that caters to businesses of all sizes and across geographies. Whether you require rapid integration with major public cloud platforms like AWS or Azure or seek to create cloud applications from the ground up, our expertise ensures tailored solutions aligned with your unique requirements.
As certified service partners for AWS and Microsoft Azure, Rishabh Software assists you in creating and running cloud-native applications, leveraging distributed computing as per the cloud delivery model.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How Organizations Can Use the Best of Both Edge and Cloud Computing?
A: Edge computing helps process data closer to where it’s generated, reducing delays, and saving bandwidth. Meanwhile, cloud computing offers vast storage and powerful processing capabilities. To utilize both effectively, companies can use fog/edge computing for real-time tasks, like immediate data analysis, and the cloud for storage, complex computations, and long-term data analysis.
Q: What is the Future of Edge Computing and Cloud Computing for IoT?
A: The future of IoT will likely see a hybrid mixture of edge and cloud computing. Edge computing will handle quick, time-sensitive tasks closer to where devices operate, ensuring faster responses.
Whereas cloud computing will manage data storage, complex analysis, and long-term trends. Together, they’ll form a powerful duo, ensuring efficient and reliable IoT operations.
Q: How does Cloud Computing Work?
A: Cloud Computing acts as a virtual processing and storage hub. Rather than depending solely on your device, it utilizes internet-connected remote servers to store data and run applications. Your device accesses these servers via the internet, allowing you to use software, store data, and perform tasks without requiring high-powered hardware.
Q: How Does Edge Computing Work?
A: It involves processing data closer to where it’s created, rather than in a centralized location.
Edge devices process data on-site immediately which reduces the need to send all information to a distant data center. This results in faster response times, decreased data transfer, and efficient handling of time-sensitive tasks.