Business meetings hail the IoT as a game-changer, yet behind closed doors, it’s often hushed as a data security nightmare.
IoT delivers new ways to boost business efficiency and leverage valuable business insights but also creates frightening new vulnerabilities. According to a report, 96% of surveyed organizations are struggling to secure their IoT and connected devices to some degree. While 89% say their organization’s IoT and connected products have been hit by cyberattacks at an average cost of $250k[1].
Is your business fully prepared to tackle IoT security challenges? If not, IoT-related breaches and outages can disrupt your operations, negatively affect customer trust, and even damage your company’s reputation! The stakes are high and the room to make mistakes is minimal. It’s time you know the key challenges of securing IoT devices and the best practices to secure the devices, data, and networks within your IoT environments.
What is IoT Security?
Connected devices lack robust security which increases the risk of internet of things security problems. The term IoT Security covers different techniques, processes, and practices designed to shield IoT devices from security breaches and address problems like:
- Ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access systems.
- Protecting sensitive data in transit and at rest.
- Keeping devices up-to-date with patches and updates.
- Securing communication channels between devices and networks.
- Implementing strategies for timely updates, even with limited device control.
Enterprises need robust IoT security strategies that cover:
- Physical security: Protecting devices from physical tampering.
- Application security: Securing software and firmware.
- Data security: Protecting data confidentiality and integrity.
- Network security: Securing communication channels and preventing unauthorized access.
Why is IoT Security Important?
The recent Keyfactor report states that IoT connections are likely to grow from $16.7[2] billion in 2023 to $29 billion IoT connections by 2027. With critical sectors as diverse as healthcare, manufacturing, financial services, smart cities, and government rapidly depending on connected devices to conduct their daily operations, it is no surprise that security has become a top priority. The growing number of IoT-connected devices are equipped to share sensitive data across a broad network which could pose a serious threat for individuals, companies and nations if compromised.
Here are compelling reasons why IoT security issues should be a top priority:
- Since IoT-connected devices share sensitive data, therefore, data leaks and breaches pose not just legal risks but also significant financial losses.
- IoT security issues can potentially disrupt system operations, leading to costly service downtime that disrupts business continuity.
- A security breach can damage a company’s reputation and negatively impact the trust of its clients and stakeholders.
- IoT devices are susceptible to being hijacked into botnets which further increases the risk of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and other automated cyberthreats.
- Given that some IoT devices are deployed in healthcare or human protection scenarios, their security is not just a business concern but a crucial matter concerning people’s safety.
Traditionally, IoT security has three main goals, also known as the CIA Triad:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized individuals or devices can access sensitive business data, especially in private settings like hospitals and homes.
- Integrity: Maintaining the consistency, accuracy, and trustworthiness of data throughout an IoT device’s life cycle.
- Availability: Ensuring that IoT services and applications are consistently available to authorized individuals or devices.
Our ultimate guide on IoT testing explores the benefits, challenges, and framework underpinning the IoT testing process to help you mitigate potential IoT security risks.
IoT Security Challenges
In 2018 the incidents of IoT cyberattacks were only 32 million but by 2022, this number reached 112 million[3] globally. By 2023, the weekly attacks targeting IoT devices increased by 41%[4] as compared to the previous year. Not prioritizing cybersecurity when developing IoT solutions can prove to be costly and critical for your products and users.
To ensure the security of connected systems, you must be fully aware of potential IoT security risks. Below is an overview of the prevalent challenges of securing IoT devices:
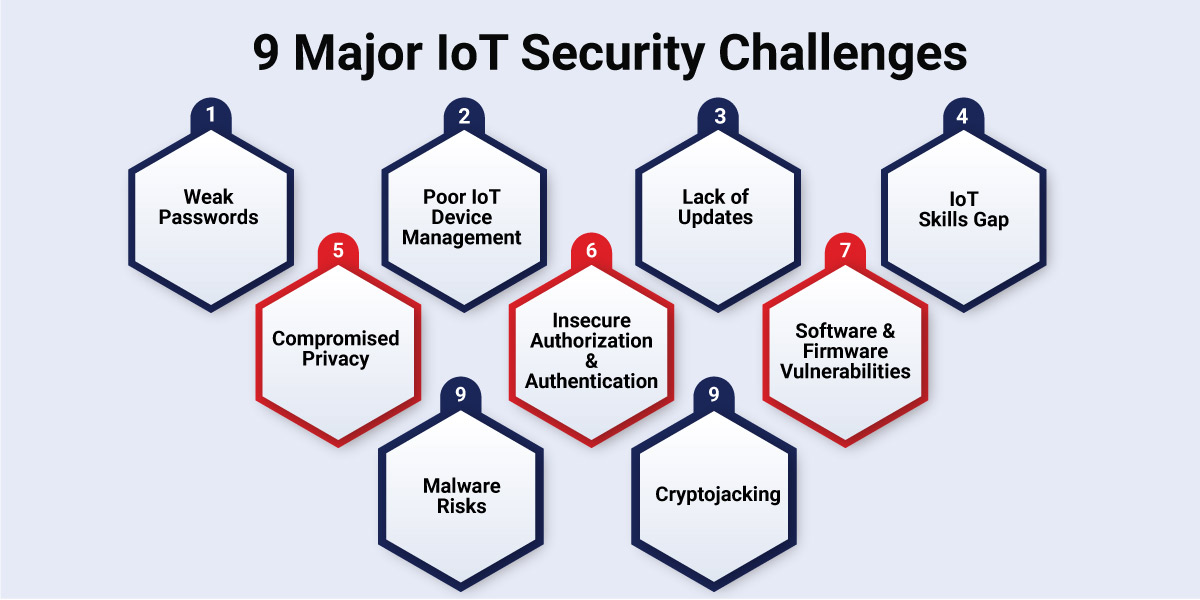
1. Weak Passwords
Many device installation executives often overlook the critical step of changing default logins and passwords for IoT devices. Default credentials, frequently left unchanged, expose IoT devices and networks to high risks. Therefore, weak and default passwords are a primary concern, as hackers exploit preset passwords and use brute force techniques to gain unauthorized access to IoT devices. This can compromise the safety of the entire connected network.
2. Neglecting IoT Device Management
In the creation of expansive networks of IoT devices, the aspect of ensuring security compatibility among these devices is often neglected. Several reasons such as unpatched vulnerabilities, lack of visibility and control often act as backdoors for attackers to exploit and blind spots, making it difficult to track suspicious activity. Various sectors, such as maritime, mining, healthcare, and retail, host numerous IoT devices with diverse manufacturers, firmware, and security requirements. Legacy devices, often integrated into these complex networks, become a major source of IoT security concerns. Hackers exploit such devices to infiltrate the network.
3. Exposed Vulnerabilities Due to Lack of Updates
Outdated firmware, insecure update deployment, and legacy operating systems pose a major threat to the entire network. This can give rise to IoT security issues and create opportunities for large-scale attacks. Enterprises using third-party hardware and software in the supply chain are particularly susceptible due to deprecated libraries and insecure software components. They can compromise both the device and its connected network. The absence of regular security patches and firmware updates can make the situation even worse.
4. IoT Skills Gap
Despite significant investments in establishing efficient IoT networks and operations, many enterprises face a skills gap among their employees that adversely impacts business operations. Lacking the necessary skills to manage, monitor, and extract maximum benefits from IoT devices can also expose digital assets to various IoT security challenges.
5. Compromised Privacy
Data, often referred to as the new oil, attracts hackers seeking vulnerabilities in networks. Poorly managed data with inadequate protection becomes an easy target for independent hackers and groups. This can lead to data exfiltration, ransom demands, or public exposure.
6. Insecure Authorization and Authentication
Proper authorization and authentication of devices are crucial for an enterprise’s IoT network. Unauthenticated devices infiltrating enterprise networks pose a significant threat, as seen in cases involving tech giants like Tesla and heightened challenges in the healthcare sector.
7. Software and Firmware Vulnerabilities
IoT systems often face security concerns due to a lack of computing resources for security functions. IoT security risks arise from various factors, including weak access control, limited budgets for testing and improving firmware security, infrequent patches and updates, user neglect in updating devices, and poor protection from physical attacks during assembly. Malicious actors leverage these loopholes to compromise communications, install malware, and steal valuable data.
8. Malware Risks
Common IoT devices susceptible to malware attacks include smart home appliances, security cameras, and medical devices. IP cameras are particularly risky due to their constant exposure to the internet and often weak passwords. If malware infiltrates an IoT system, it can compromise functionality, collect personal data, and launch various attacks.
9. Cryptojacking
Companies must constantly track the processing power their IoT devices use. Since IoT devices have less robust security, hackers are now creating large IoT botnets for cryptocurrency mining. They inject malware into IoT devices, harnessing their combined power for intensive mining. The hidden nature of cryptojacking poses a big threat to all kinds of businesses.
IoT Security Best Practices
Enhancing the security of your IoT systems involves implementing best practices to bolster the three core components: devices, networks, and data. Understanding the intricacies of your infrastructure, including devices and servers, while continuously monitoring their statuses, is the key. Here are key best practices for IoT security to protect your IoT systems:
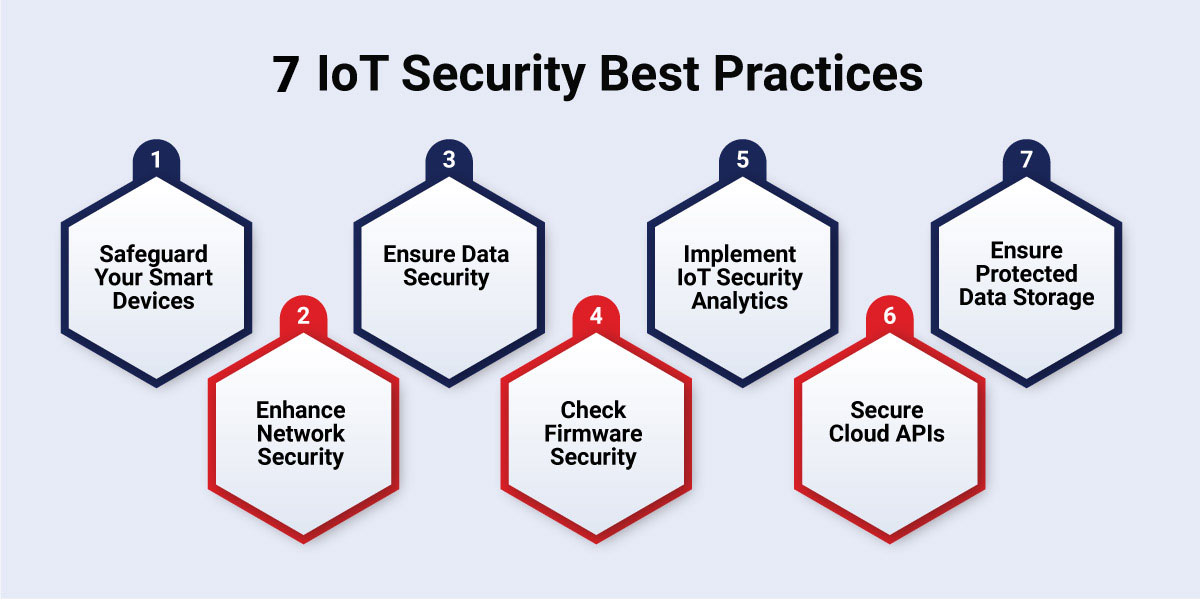
1. Safeguard Your Smart Devices
Ensure the security of your smart devices by implementing the following measures:
- Device Authentication: Ensure every IoT device has a unique identity. It helps to quickly identify devices causing IoT security issues by assigning unique identifiers.
- Tamper-Resistant Hardware: Safeguard against theft and tampering by incorporating tamper-resistant hardware security features like Trusted Platform Modules (TPM) or Hardware Security Modules (HSM) for secure cryptographic operations and key storage.
- Patches and Updates: Ensure constant updates and patches to ensure ongoing device security.
- Thorough Testing: Regularly test the devices and conduct penetration testing to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Data Protections: Implement robust data protection mechanisms, including secure storage of cryptographic keys.
- Component Performance: Ensure that IoT devices meet performance requirements, offering efficient usability and connectivity even during internet disruptions.
2. Enhance Network Security
Overcome the challenges of diverse protocols with the following strategies:
- Strong Authentication and Access Controls: Implement unique default credentials and, if possible, multi-factor authentication to limit the device’s capabilities based on role and necessity.
- Encryption and Secure Protocols: Ensure secure communication between devices using adapted cryptographic algorithms and industry-standard protocols like TLS/SS.
- Minimize Device Bandwidth: Limit network traffic, detect suspicious activity, and protect against DoS attacks.
- Segmented Networks: Divide large networks into segments, restricting access to minimize the impact of breaches.
- API Safety: Since APIs serve as a primary gateway for data exchange between IoT devices and applications, it is a good practice to regularly check and secure APIs to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Ensure Data Security
Uphold the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data across IoT environments:
- Protect Sensitive Information: Use unique default passwords, robust authentication, and mechanisms for data deletion.
- Collect Only Necessary Data: Minimize data collection to reduce the risk of leaks and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Secure Network Communications: Restrict unnecessary communication and employ encryption methods optimized for IoT systems.
- Use Digital Certificates: Employ digital certificates for secure data transmission and identity verification.
4. Check Firmware Security
Mitigate IoT security concerns by securing device firmware on multiple levels:
- Compile Time Security: Ensure secure code at compile time with obfuscation, safe stack operations, and data wiping.
- Runtime Protection: Monitor binary code and data integrity during runtime to detect intrusions.
- Firmware Integrity: Employ encryption, digital signatures, and regular updates to maintain firmware integrity.
- Security Testing: Conduct thorough software security testing, including penetration testing and code audits.
5. Implement IoT Security Analytics
Utilize telemetry data for real-time analysis to detect anomalies and ensure a robust IoT ecosystem:
- Detect Anomalous Behavior: Identify unusual traffic spikes and changes in device configurations.
- Identify Security Vulnerabilities: Security analytics tools help in detecting known and emerging vulnerabilities or threats in firmware, software, and networks.
- Investigate Security Incidents: Respond to security incidents like potential breaches in real-time to understand and mitigate potential damage.
- Prevent Future Attacks: Develop new security strategies based on insights gained from past attacks.
6. Secure Cloud APIs and Endpoint Protection
Protect cloud APIs and harden IoT devices against potential threats:
- Cloud API Security: Secure cloud APIs using authentication, encryption, tokens, and API gateways.
- Endpoint Protection: Harden endpoints by addressing vulnerabilities, securing high-risk ports, and safeguarding against malicious code injection.
7. Ensure Protected Data Storage
Safeguard sensitive data generated by IoT devices:
- Effective Antivirus Solutions: Implement updated antivirus solutions and monitoring tools for real-time threat prevention.
- Flexible Reporting and Scanning: Utilize features like flexible reporting, scanning, and notification systems for comprehensive network activity visibility.
- Centralized Management: Employ a centralized management console for deep insights into network security and management.
Ensuring IoT Security with Rishabh Software
As an experienced internet of things application development company, we have a team of seasoned professionals specializing in embedded and IoT application development. We provide a comprehensive range of services to meet the specific needs of your business or to develop a custom IoT system tailored to your unique specifications. With a commitment to delivering the most secure results for your business, we assure you a comprehensive solution aligned with industry best practices.
Our IoT security practices start with safeguarding your devices and extend seamlessly into your network environment. Once an IoT device is secured and seamlessly integrated into the network, our holistic approach ensures coordinated protection across all network elements. This encompasses secure connectivity between devices, foolproof data storage, and safeguarding IT environments, whether on-premise or in the cloud. Rishabh Software stands as your trusted partner, ready to shield your digital ecosystem against potential threats and vulnerabilities inherent in IoT systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What happens if IoT security challenges are not addressed?
A: Treating IoT security as an afterthought or inability to address IoT security challenges can have the following results:
- Loss of data
- Disruption of asset availability, leading to extended downtimes
- Hackers may release your stolen data or user credentials on the web, triggering secondary attacks
- Data breaches can expose sensitive information like personal data, financial records, or trade secrets
- Unauthorized control of devices for malicious purposes such as botnets or ransomware attacks
- Attacks on critical infrastructure leading to power outages, transportation disruptions, or healthcare system failures
- Security failures resulting in a loss of trust and damage to business repute.
Q: Which types of connected devices are most susceptible to IoT security risks?
A: The most susceptible potential targets are:
- Devices with weak passwords or no authentication
- Devices with outdated software
- Devices lacking encryption make data easy to intercept
- Devices with poor physical security are vulnerable to tampering or theft.
Q: What are examples of attacks on IoT systems and devices?
A: The most common examples of attack on IoT devices include:
- Attacks targeting communications between IoT devices and servers to compromise or steal data.
- Exploiting firmware vulnerabilities or taking advantage of weaknesses in an IoT device’s operating system.
- Credential-based attacks using default administrator usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access.
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks intercepting unencrypted communications between trusted entities.
- Physical hardware-based attacks focusing on the chip in the IoT system to take control of the device.
- Gaining network access and stealing data to use it as a launchpad for other attacks.
Footnotes:
1. https://www.keyfactor.com/state-of-iot-security-report-2023
2. https://iot-analytics.com/number-connected-iot-devices
3. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1377569/worldwide-annual-internet-of-things-attacks







